Thyroid nodules are overgrowths of thyroid cells that form a lump within the thyroid gland10. Nodules are common entities in the thyroid and most of the time, they are harmless and do not produce any symptoms. In fact, according to American Thyroid Association (ATA), only 40% of the patients with thyroid nodules exhibit some level of symptoms1. The precise cause of most thyroid nodules remains unknown. Today, we are going to cover some medical conditions that are associated with the development of thyroid nodules.
Risk Factors for Thyroid Nodules
- Gender: Women are more likely to have thyroid nodules than men. In fact, 1/8 of women will develop some form of thyroid disease during their lifetime1.
- Age: The likelihood of getting thyroid nodules increases as you age.
- Family History: Other family members with thyroid conditions increases your chance of getting thyroid disease.
- Radiation Exposure: Prior exposure to radiation from medical treatment to the head and neck area may increase your chance of developing nodules.
Medical Conditions That Can Cause Thyroid Nodules
The underlying cause of everyone’s thyroid nodule varies. Below are several conditions that are associated with nodular development in your thyroid gland.
Thyroid Hyperplasia (Goiter)
Diffuse thyroid hyperplasia is the enlargement of the thyroid gland due to an increase in the reproduction rate of the thyroid tissue. Enlargement of the thyroid gland is also known as goiter. Thyroid hyperplasia accounts for 80% of all nodular thyroid disease13. It has many causes including iodine deficiency and thyroid autoimmune diseases13. The goiter could result in:
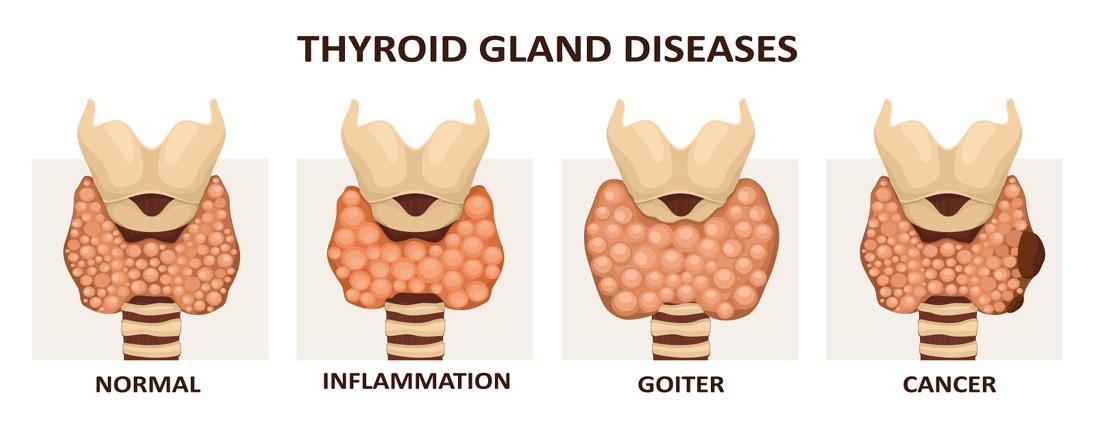
- Hyperthyroid: overproduction of thyroid hormones
- Euthyroid: normal production of thyroid hormone
- Hypothyroid: underproduction of thyroid hormone
Thyroid Adenoma
Thyroid adenomas are benign lesions (tumors) of the thyroid gland. They account for 5-10% of all nodular disease of the thyroid13. About less than 10% of thyroid adenomas are hyper-functional with the overproduction of thyroid hormone causing the nodules to be toxic (hyperthyroidism)13. The majority of thyroid adenoma functions normally, producing a normal level of thyroid hormone (euthyroid)13.
Autoimmune Diseases
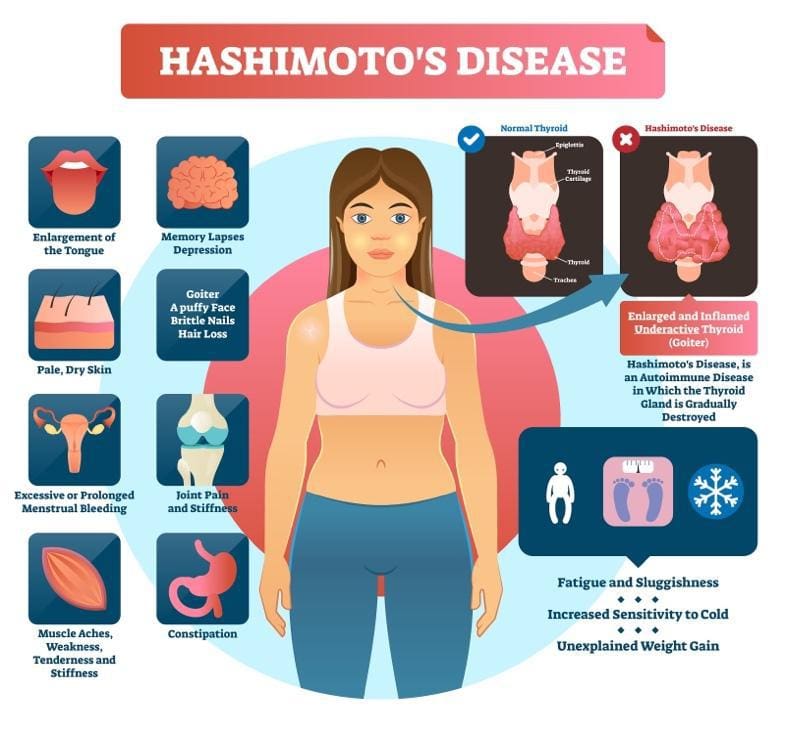
There are two autoimmune conditions that can predispose (cause) a thyroid gland to develop thyroid nodules: Hashimoto Disease and Grave’s Disease. Both conditions can associate with goiter as a result of an underactive or overactive thyroid.
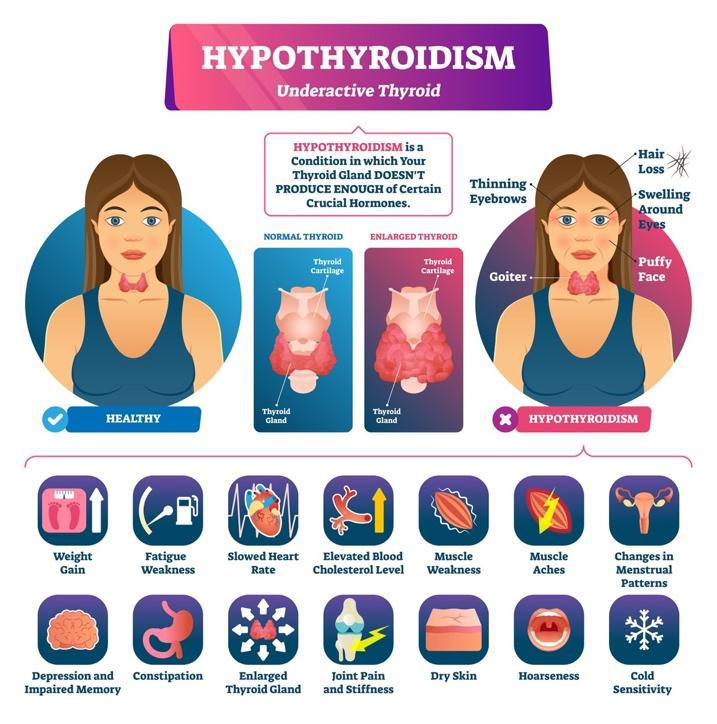
Hashimoto Disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland causing inflammation (thyroiditis). As a result, the ability of the thyroid gland to produce hormones becomes reduced and this leads to a condition called hypothyroidism. In an average person, thyroid hormones T3 and T4 are required for many vital bodily functions such as metabolism. Hence, reduced production of thyroid hormones slows down many bodily functions, causing a range of undesired symptoms that are associated with the body having too little energy.
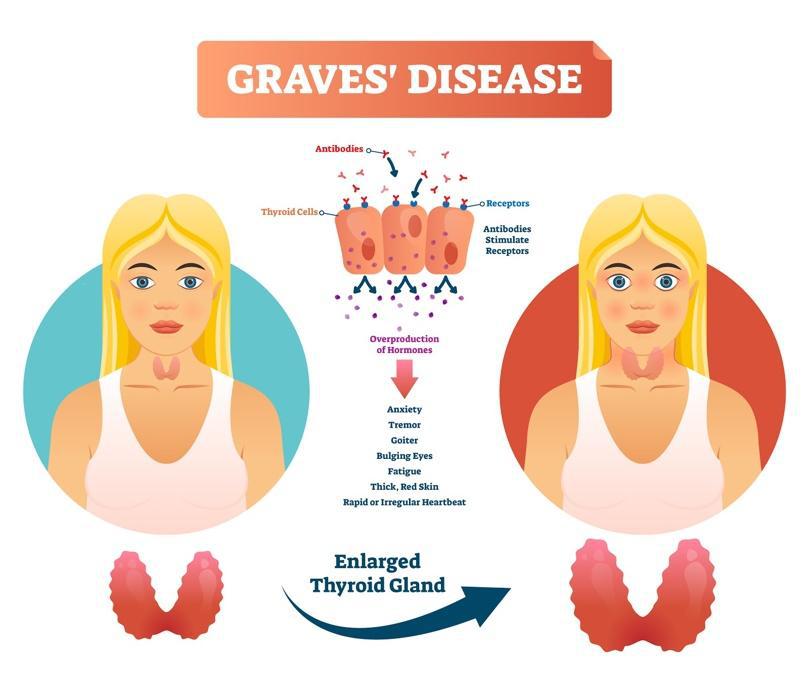
Grave’s Disease is another autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland causing overproduction of the thyroid hormone. This condition is known as hyperthyroidism. Increased thyroid hormone production causes symptoms that are associated with the body having too much energy.
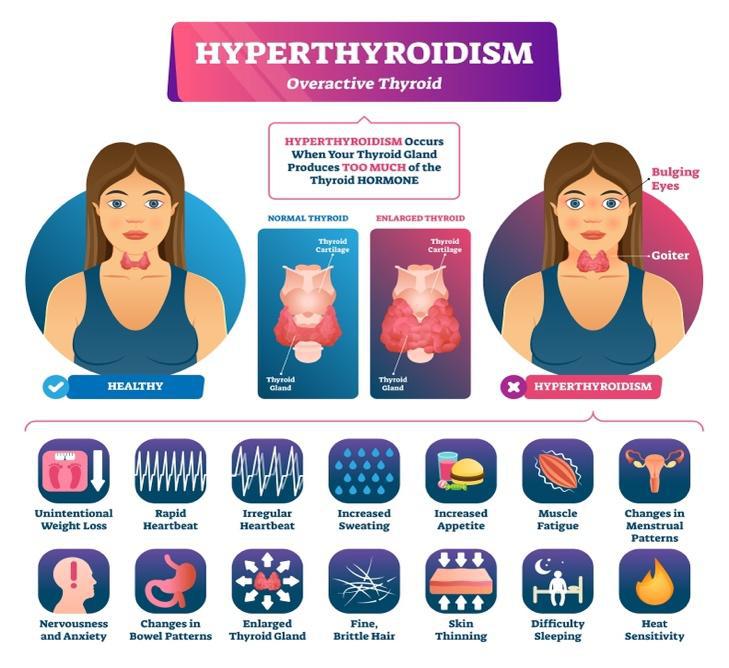
Thyroid Cancer
Lastly, malignancy (cancer) is the most unwanted cause for any thyroid nodules, and they occur in 5-10% of all thyroid nodules<sup>12</sup>. There are several types of thyroid cancer including Papillary Cancer (PTC), Follicular Cancer (FTC), Medullary Cancer (MTC), and Anaplastic Cancer (ATC). Most thyroid cancers respond well to treatment with a good prognosis rate, though some very rare thyroid cancer can be aggressive13.
Thyroid nodules are very common entities and according to ATA, about 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid diseases1. Fortunately, most thyroid nodules are asymptomatic and benign. To learn more about your thyroid issues, speak to a specialist today!
#thyroidnodule #Hashimotos #Graves #Hyperthyroidism #Hypothyroidism

5 Responses
I have every symptom for thyroid issues but my blood work is ok
Hi, my doctor (general) told me that I don’t have autoimmune diseases, but he didn’t look at the previous doctor exams where there are autoantibodies and nodules (ultrasound), but the thyroid hormones are still in the range of “normal” – my rheumatologist says that I have Hashimotos – my question is: is it an autoimmune disease or not? Note: the doctor is not cooperative and I’m tired of searching for one that really listen to me, seems that nowadays doctors don’t want to waste time thinking and searching for scientific answers. Until now I’m applying by myself supplements protocols for Hashimoto and mitochondrial dysfunction. Thanks in advance for your answer.
Hello Christina,
I’m very sorry to hear what you have been through. But we cannot give any medical advices. If you can tell me your location, I can try to recommend a few very good Thyroid RFA specialist in your area to help you out.
Best,
RFA for Life
Hi Christina – Sorry you’re going through “the dance” with your doctor. The bottom line is this – If you have TPO antibodies, you DO have Autoimmune Hashimoto’s. I tested positive for TPO last year after I started having weird symptoms and started having pain in my throat. All of my thyroid “numbers were normal”. After an ultrasound of my thyroid, it was revealed that I had a single nodule and an enlarged thyroid (goiter). They told me not to worry about it and to follow up in 12 mo. I did not take their advice and continued to seek help. A 2nd ultrasound and review revealed the need for a biopsy and the biopsy revealed Papillary Carcinoma. In my research, I’ve found that thyroid cancer is often associated with single nodules less that 2cm. I opted to have my thyroid removed which basically took care of the cancer, Hashimoto’s and the goiter. The other bottom line with Hashimoto’s is this … your doctors can’t/won’t do anything for you until your TSH, T4,T3 numbers blow up. Sadly, if they can’t give you a pill, then as far as they’re concerned nothing is wrong with you. You know your body and when something isn’t right. I wish you the best and hope you can find someone in the medical community to help you.
Hi Kim
Can I know what were your symptoms other than having pain ? I have a very high TPO , with minimum dosage of thyroxine I am in upper limits of normal TSH range. Having single nodule over 1.5cm. I am feeling exhausted most often, especially with little physical activities. All typical characteristics of hypothyroidism, but doctor keeps saying it is not related because TSH is yet within normal range. Worried if this nodule is causing more trouble than thought.